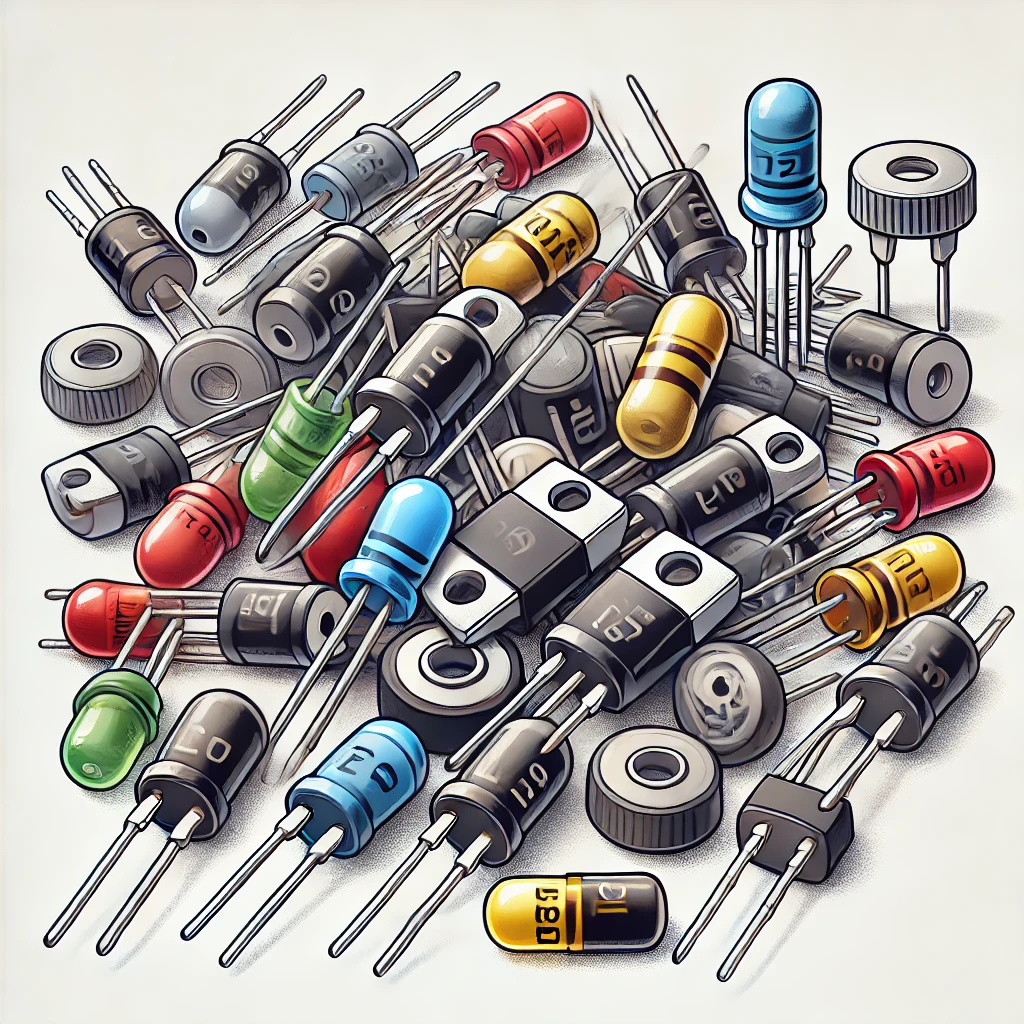
A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in only one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. It acts like an electronic one-way valve and is widely used in rectifiers, signal processing, voltage regulation, and protection circuits.
📜 History of the Diode
1️⃣ Early Crystal Detectors (1904-1910)
- The first diodes were crystal detectors, also known as cat’s whisker diodes, used in early radio receivers.
- These were made from galena (lead sulfide) crystals and a fine metal wire to detect radio signals.
2️⃣ Vacuum Tube Diodes (1904, John Ambrose Fleming)
- The first practical vacuum tube diode was invented by John Ambrose Fleming in 1904.
- It was used in radio communications and early electronics.
3️⃣ Semiconductor Diodes (1940s-Present)
- The first semiconductor diodes (made from germanium and silicon) replaced vacuum tubes.
- Silicon diodes (1950s-present) became the standard due to better efficiency and durability.
🔹 Types of Diodes and Their Applications
1️⃣ Rectifier Diodes
📌 Purpose: Converts AC to DC in power supplies.
📌 Example: 1N4007 (General-purpose rectifier)
✅ Application:
- Power adapters (converting AC mains to DC for electronics).
- Battery chargers for phones and laptops.
✅ Example Circuit (Bridge Rectifier for Power Supply):
AC Input → [Bridge Rectifier] → DC Output
- Uses four diodes to convert AC voltage into DC voltage.
2️⃣ Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
📌 Purpose: Emits light when current flows through it.
📌 Example: Red, Green, Blue (RGB) LEDs, Infrared LEDs
✅ Application:
- Indicator lights in devices.
- Car headlights and tail lights.
- TVs and display screens (LED backlighting).
✅ Example Circuit (Simple LED Circuit):
(5V) → [Resistor] → [LED] → GND
- The resistor limits current, protecting the LED from damage.
3️⃣ Zener Diodes
📌 Purpose: Provides voltage regulation by maintaining a constant voltage.
📌 Example: 1N4733A (5.1V Zener diode)
✅ Application:
- Voltage regulation circuits (protecting circuits from overvoltage).
- Microcontroller voltage reference (Arduino, ESP32).
✅ Example Circuit (Voltage Regulator):
(12V) → [Zener Diode 5.1V] → GND
- Limits voltage to 5.1V, protecting sensitive components.
4️⃣ Schottky Diodes
📌 Purpose: Used in high-speed switching and low voltage drop applications.
📌 Example: 1N5819 (Schottky diode for power circuits)
✅ Application:
- Efficient power supplies (DC-DC converters, solar panels).
- Fast-switching circuits (RF and digital electronics).
✅ Example Circuit (Fast Rectifier in Power Supply):
(AC Power) → [Schottky Diode] → (DC Load)
- Lower voltage drop (~0.2V) improves efficiency.
5️⃣ Photodiodes
📌 Purpose: Converts light into electrical current (used in sensors).
📌 Example: BPW34 (Light sensor photodiode)
✅ Application:
- Solar panels (converting sunlight to electricity).
- IR sensors (remote controls, motion detectors).
- Camera light sensors (adjusting brightness automatically).
✅ Example Circuit (Light Detection):
(Photodiode) → (Microcontroller ADC Pin)
- Generates voltage based on light intensity.
6️⃣ Tunnel Diodes
📌 Purpose: Used in high-frequency and microwave applications.
📌 Example: 1N3716 (Tunnel diode for microwave oscillators)
✅ Application:
- High-speed computers.
- Microwave and radio-frequency (RF) circuits.
✅ Example Circuit (RF Oscillator):
(Oscillator Circuit) → [Tunnel Diode] → (RF Output)
- Produces stable high-frequency signals.
7️⃣ Varactor (Variable Capacitance) Diodes
📌 Purpose: Used in tunable circuits (radio tuning, frequency modulation).
📌 Example: BB212 (Tuning diode for radios and TVs)
✅ Application:
- FM Radio tuning circuits.
- Voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs).
✅ Example Circuit (Tuning Circuit):
(Antenna) → [Varactor Diode] → (Tuning Circuit)
- Adjusting voltage changes capacitance, tuning the frequency.
8️⃣ Laser Diodes
📌 Purpose: Emits a coherent laser beam (used in optical devices).
📌 Example: CD/DVD Player Laser Diodes
✅ Application:
- Laser pointers and barcode scanners.
- CD/DVD/Blu-ray players.
- Fiber-optic communication systems.
✅ Example Circuit (Laser Pointer):
(Battery) → [Resistor] → [Laser Diode] → GND
- Controls power to prevent overheating.
🔹 Summary of Diode Types and Applications
| Type of Diode | Function | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
| Rectifier Diode | Converts AC to DC | Power supplies, chargers |
| Light-Emitting Diode (LED) | Emits light | Displays, indicators |
| Zener Diode | Regulates voltage | Voltage protection |
| Schottky Diode | Fast switching, low voltage drop | Power efficiency, solar panels |
| Photodiode | Converts light to electricity | Light sensors, solar panels |
| Tunnel Diode | High-speed switching | Microwave circuits |
| Varactor Diode | Variable capacitance | Radio tuning |
| Laser Diode | Emits laser light | Optical storage, barcode scanners |
⚡ Conclusion
Diodes play a critical role in modern electronics, from power conversion to light emission and high-speed communication. Whether you’re working on a power supply, radio circuit, or optical system, diodes are essential components that shape modern technology.