Capacitors play a crucial role in power supply filtering by stabilizing voltage, reducing noise, and improving power quality. Let’s break it down step by step.
1. Why Are Capacitors Used in Power Supplies?
Power supplies often have voltage fluctuations, noise, and ripple due to factors like AC-to-DC conversion, sudden load changes, and electromagnetic interference (EMI). Capacitors help in:
- Smoothing DC output after rectification.
- Filtering high-frequency noise (EMI).
- Stabilizing voltage for steady power delivery.
- Reducing ripple voltage in AC-to-DC converters.
2. Types of Capacitors Used in Power Supply Filtering
Different types of capacitors are used based on frequency response, capacitance value, and application:
| Capacitor Type | Function in Filtering | Common Placement |
|---|---|---|
| Electrolytic Capacitors | Bulk energy storage, smoothing large ripples | Across rectified DC output |
| Ceramic Capacitors | High-frequency noise filtering | Close to IC power pins |
| Tantalum Capacitors | Stable low-ESR filtering | Power rails of sensitive circuits |
| Film Capacitors | High-frequency AC filtering | Across transformer outputs |
3. Capacitor Placement in a Power Supply
🔹 Basic AC-DC Power Supply Filtering
A typical linear power supply consists of a transformer, rectifier, filter capacitors, and voltage regulators.
(A) Smoothing Capacitor (Bulk Filtering)
After the bridge rectifier, the DC voltage has a ripple. A large electrolytic capacitor is placed across the output to smooth the voltage.
where:
- Function: Converts pulsating DC into a more stable DC.
- Formula for Capacitance Selection:
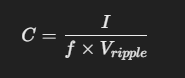
- where:
- I = Load current (A)
- f = Ripple frequency (Hz) (Twice the AC mains frequency after full-wave rectification)
- V_ripple = Allowable ripple voltage (V)
(B) Decoupling Capacitor (Noise Filtering)
- A small ceramic capacitor (0.1µF – 1µF) is added in parallel with the electrolytic capacitor.
- Why? Electrolytic capacitors are not good at filtering high-frequency noise, but ceramics respond faster to voltage changes.
🔹 Capacitors in Switching Power Supplies (SMPS)
Switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) use high-frequency switching, so capacitor selection is critical.
(A) Input Capacitors (EMI Filtering)
- Before the switching circuit, a film capacitor or electrolytic capacitor reduces mains noise.
- Sometimes X and Y safety capacitors are used for EMI suppression.
(B) Output Capacitors (Low ESR for Ripple Reduction)
- Low ESR capacitors (like tantalum or ceramic) are placed at the output of SMPS regulators to reduce ripple.
(C) Bypass Capacitors (For ICs & Microcontrollers)
- Every microcontroller (e.g., Arduino R4 WiFi) needs a 0.1µF ceramic capacitor near VCC and GND to suppress noise.
- Without these, microcontrollers may reset due to power spikes.
4. Choosing the Right Capacitor for Power Filtering
🔹 What Factors Matter?
- Capacitance Value (µF)
- Higher = better filtering, but too large can slow response time.
- Voltage Rating
- Always choose at least 1.5× the expected voltage (e.g., for 5V circuits, use a 10V-rated capacitor).
- ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance)
- Low ESR capacitors (e.g., tantalum, polymer) are best for switching power supplies.
- Temperature & Lifetime
- Electrolytics degrade over time; ceramics last longer.
5. Example Circuits
🔹 Linear Power Supply with Capacitors
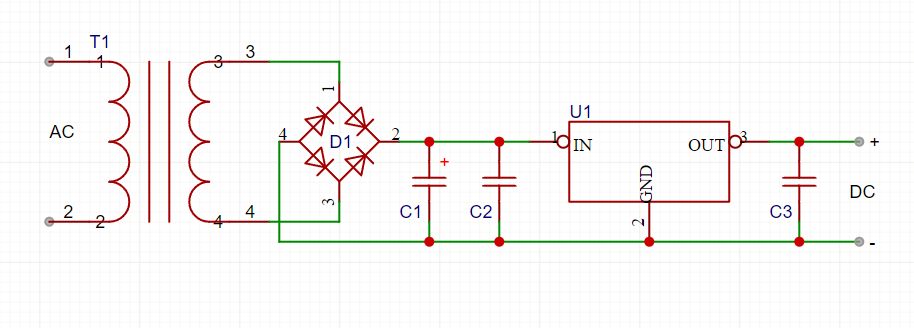
- Electrolytic capacitor C1 (1000µF, 25V) smooths DC after rectification.
- 0.1µF ceramic capacitor C2 near the voltage regulator reduces high-frequency noise.
🔹 Switching Power Supply (Buck Converter)
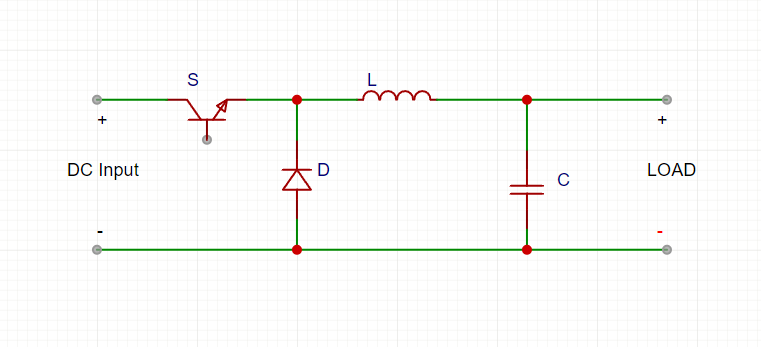
- Electrolytic or Polymer capacitor (Low ESR) filters output ripple.
- Ceramic capacitors reduce high-frequency noise.
Conclusion
Capacitors are essential in power supplies to filter ripples, reduce noise, and stabilize voltage. Using a combination of electrolytic, ceramic, and low ESR capacitors ensures optimal performance.