A transformer is an electrical device that transfers electrical energy between circuits using electromagnetic induction. It works by converting voltage levels without changing the frequency of the current. Transformers are essential in power distribution, electronics, and signal processing.
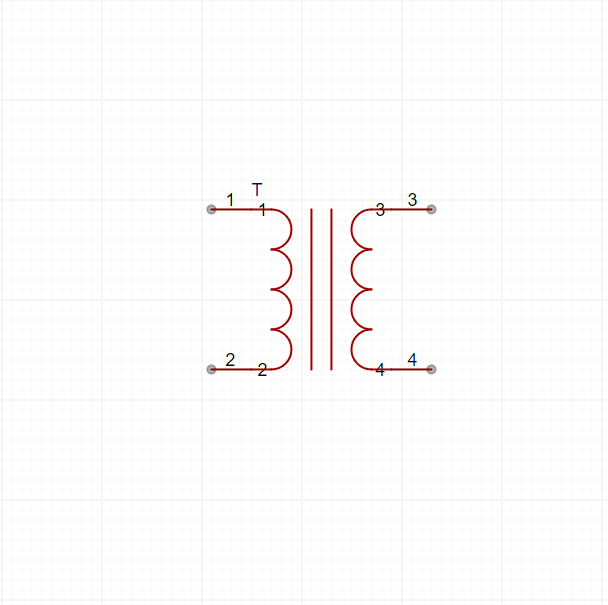
📜 History of Transformers
1️⃣ Early Discoveries (1831-1885)
- Michael Faraday (1831) discovered electromagnetic induction, laying the foundation for transformers.
- Lucien Gaulard and John Dixon Gibbs (1882) developed the first practical transformer.
- Nikola Tesla (1885-1887) improved transformer designs for AC power transmission.
2️⃣ Industrial Adoption (1890s-1900s)
- George Westinghouse used transformers in the first AC power grid (1893).
- Transformers became crucial in long-distance power transmission.
3️⃣ Modern Developments (20th-21st Century)
- High-voltage transformers enabled national and global power grids.
- Electronic transformers developed for computers, telecom, and automation.
🔹 Types of Transformers & Their Applications
1️⃣ Power Transformers

📌 Purpose: Used in power generation and distribution to step-up or step-down voltage.
📌 Examples:
✅ Step-Up Transformer (Increases voltage for long-distance transmission).
✅ Step-Down Transformer (Reduces voltage for safe domestic and industrial use).
✅ Application:
- Power grids
- Industrial plants
- Substations
2️⃣ Distribution Transformers
📌 Purpose: Reduces voltage for commercial and residential use.
📌 Example: Pole-mounted transformers for homes (Step-Down Transformers).
✅ Application:
- Provides 220V or 110V for home appliances.
- Used in factories and commercial buildings.
3️⃣ Instrument Transformers
📌 Purpose: Used for measuring and protection in power systems.
📌 Examples:
✅ Current Transformer (CT) – Measures high current levels safely.
✅ Potential Transformer (PT) – Measures high voltage levels accurately.
✅ Application:
- Electric meters (for billing and monitoring).
- Power grid fault detection.
4️⃣ Auto-Transformers
📌 Purpose: Uses a single winding for voltage regulation.
📌 Example: Variable voltage transformers (Variac).
✅ Application:
- Voltage regulators for AC motors and trains.
- Testing laboratories for controlled power supply.
5️⃣ Isolation Transformers
📌 Purpose: Electrically isolates circuits for safety and noise reduction.
📌 Example: 1:1 Ratio Transformer (Same Input & Output Voltage).
✅ Application:
- Medical equipment (prevents electric shocks).
- Audio systems (reduces electrical noise).
6️⃣ Pulse Transformers
📌 Purpose: Used in digital circuits for pulse transmission.
📌 Example: Ethernet LAN transformers.
✅ Application:
- Signal transmission in communication networks.
- Switching power supplies.
7️⃣ Ferrite Core Transformers
📌 Purpose: Used in high-frequency electronics (MHz-GHz range).
📌 Example: Used in SMPS (Switched Mode Power Supplies).
✅ Application:
- Laptops and phone chargers.
- RF communication circuits.
🔹 Summary of Transformer Types & Applications
| Type of Transformer | Function | Example Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Power Transformer | Steps up/down voltage in power transmission | Power grids, substations |
| Distribution Transformer | Steps down voltage for homes & industries | Electric supply to buildings |
| Instrument Transformer | Measures current & voltage | Electric meters, power monitoring |
| Auto-Transformer | Provides adjustable voltage | AC motor speed control, labs |
| Isolation Transformer | Electrical isolation & noise reduction | Medical, audio systems |
| Pulse Transformer | Transmits pulses in circuits | Ethernet, digital communication |
| Ferrite Core Transformer | Works at high frequencies | SMPS, RF circuits |
⚡ Conclusion
Transformers are essential in power systems, electronics, and automation, enabling efficient voltage conversion and signal transmission. From power stations to tiny circuits in phones, transformers shape modern electrical systems.