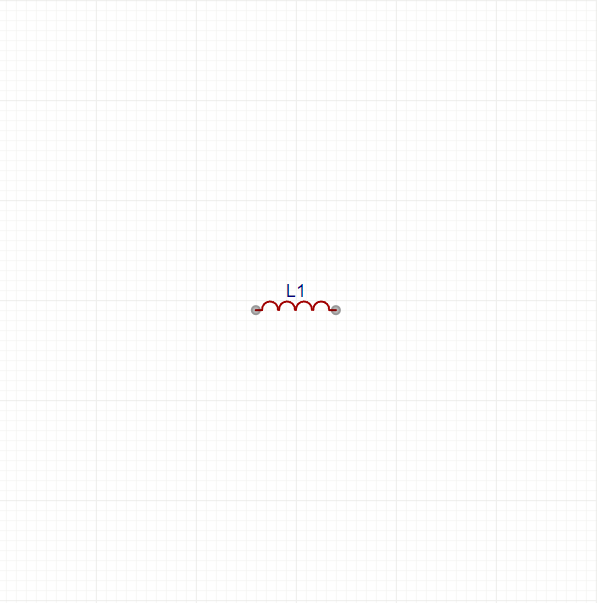
An inductor is a passive electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. It consists of a coil of wire, often wrapped around a core made of air, iron, or ferrite.
📜 History of Inductors
- 1831 – Michael Faraday discovered electromagnetic induction, the principle behind inductors.
- 1880s – The first practical inductors were developed as part of early electrical circuits.
- Early 1900s – Inductors became essential in radio and telecommunication.
- Modern Day – Used in power electronics, RF circuits, transformers, and wireless charging.
🛠 Types of Inductors
- Air-Core Inductors
- No magnetic core → Purely wire-wound.
- Used in high-frequency applications like radio antennas.
- Iron-Core Inductors
- Iron core enhances magnetic field → Increases inductance.
- Used in power transformers and audio systems.
- Ferrite-Core Inductors
- Ferrite material reduces energy loss at high frequencies.
- Used in switching power supplies, RF circuits, and EMI filters.
- Toroidal Inductors
- Donut-shaped coil → Reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Used in power supplies and audio equipment.
- Choke Inductors
- Filters out high-frequency noise in circuits.
- Used in power supplies and communication circuits.
- Variable Inductors
- Adjustable inductance by changing the core position.
- Used in tunable circuits like radio receivers.
⚡ Applications of Inductors
🔹 Power Supplies – Used in DC-DC converters and transformers.
🔹 Radio & Communication – Found in RF circuits, antennas, and signal filters.
🔹 Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Filtering – Blocks unwanted signals.
🔹 Inductive Sensors – Used in metal detectors, proximity sensors.
🔹 Wireless Charging – Transfers energy via inductive coupling.
🔹 Motors & Generators – Converts electrical energy into motion and vice versa.
🔍 Example Circuit: Inductor as a Filter
Inductors are commonly used in LC (Inductor-Capacitor) filters to smooth power signals in AC circuits.
(Vin) --- [Inductor (L)] --- (Vout) --- [Capacitor (C)] --- GND
- The inductor blocks high-frequency noise, allowing only smooth DC voltage.
- The capacitor removes any remaining ripples.