📜 Definition
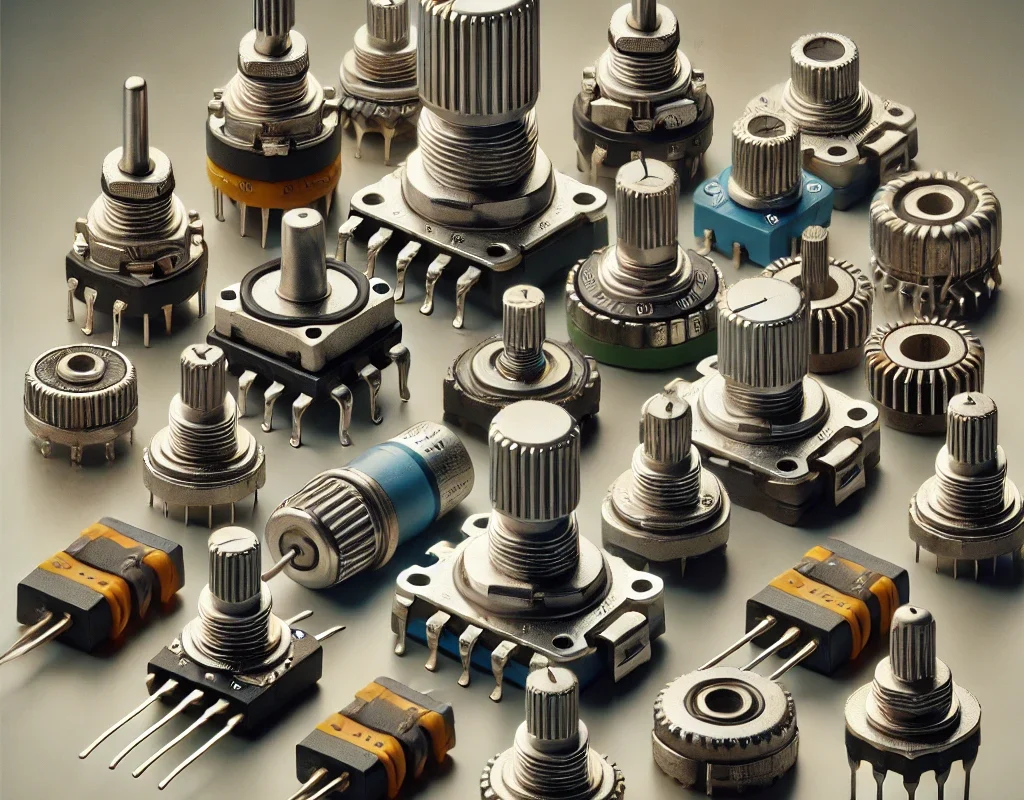
- Potentiometer:
A variable resistor with three terminals that allows you to adjust resistance and divide voltage. It’s commonly used for controlling signals like volume, brightness, or other adjustable parameters.
🔍 Key Functions
- Variable Resistance:
Adjusts resistance based on the position of its knob or slider.
- Voltage Divider:
Provides a variable output voltage proportional to the position of the control, useful for fine-tuning signal levels.
🔧 Types of Potentiometers
- Linear Potentiometers:
The resistance changes evenly across the scale.
- Logarithmic (Audio Taper) Potentiometers:
The resistance changes in a logarithmic manner, which is ideal for audio applications like volume control.
- Rotary and Slider Potentiometers:
- Rotary: Most common, where you turn a knob.
- Slider: Often used in user interfaces for more direct, linear control.
🎯 Applications
- Audio Controls:
Used in amplifiers and mixing boards to adjust volume.
- Lighting Controls:
Adjust brightness of LEDs or display backlights.
- Signal Adjustment:
Fine-tuning analog circuits for sensors, radios, and other electronics.
- User Interfaces:
Commonly found on control panels and other devices for intuitive adjustments.
📡Broadcast the signal — amplify the connection.