USB Type-C is a 24-pin reversible connector that supports power delivery, data transfer, and video output. Below is a pinout diagram and explanation of key pins.
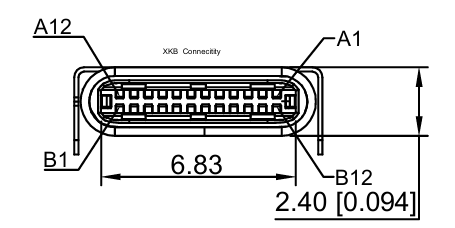
1. USB Type-C Pinout Diagram
USB Type-C has two identical rows of 12 pins, making it reversible. The key functional groups are:
┌──────────────┬──────────────┐
│ A1 GND │ B12 GND │
│ A2 TX1+ │ B11 TX2+ │
│ A3 TX1- │ B10 TX2- │
│ A4 VBUS │ B9 VBUS │
│ A5 CC1 │ B8 SBU2 │
│ A6 D+ │ B7 D+ │
│ A7 D- │ B6 D- │
│ A8 SBU1 │ B5 CC2 │
│ A9 VBUS │ B4 VBUS │
│ A10 RX2- │ B3 RX1- │
│ A11 RX2+ │ B2 RX1+ │
│ A12 GND │ B1 GND │
└──────────────┴──────────────┘
2. Key Pins and Their Functions
| Pin | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VBUS (A4, A9, B4, B9) | Power (5V to 20V) | Provides power to devices. |
| GND (A1, A12, B1, B12) | Ground | Common ground reference. |
| CC1 (A5), CC2 (B5) | Configuration Channel | Used for orientation detection and power negotiation. |
| D+ (A6, B7), D- (A7, B6) | USB 2.0 Data Lines | Standard USB 2.0 communication. |
| TX/RX (A2, A3, A10, A11, B2, B3, B10, B11) | High-Speed Data Transfer | Used for USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 communication. |
| SBU1 (A8), SBU2 (B8) | Sideband Use | Used for alternate modes (e.g., DisplayPort, Thunderbolt). |
3. USB Type-C Basic Wiring for Power
If you are using USB Type-C for power (5V output), connect:
- VBUS → 5V
- GND → GND
- CC1 or CC2 → 5.1kΩ resistor to GND (for device detection)
⚠️ Important:
- Without a 5.1kΩ pull-down resistor on CC1 or CC2, some devices may not power on.
- For USB Power Delivery (PD), you need an IC to negotiate higher voltages (e.g., 9V, 12V, 20V).
4. USB Type-C to USB 2.0 Wiring Example
To connect a USB Type-C plug to a USB 2.0 device:
USB Type-C → USB 2.0
--------------------------
VBUS (A4, B4) → 5V (Red)
GND (A1, B1) → GND (Black)
D+ (A6, B7) → D+ (Green)
D- (A7, B6) → D- (White)
CC1 (A5) → 5.1kΩ to GND
CC2 (B5) → 5.1kΩ to GND